
In comparison, there is no argument for deliberately using the TIP120 and it is essentially obsolete. This means that it can pass several Amps before it dissipates a Watt or two and you require a heatsink. The logic-level power FETs have an effective resistance rather than a voltage drop, and that resistance is quite low, specified as no more than 0.11 Ω for the IRL540 at 4 V on the gate, somewhat less with higher gate drive. The second is that if you are switching a substantial current - and that is of course why you chose the Darlington - the transistor dissipates significant power - at least 1 Watt per Amp - and needs to be provided with a heatsink, This has two consequences - you lose that voltage drop, not so significant for a 12 V or greater supply but quite a significant drop if operating at 5 Volts. The point is that a Darlington transistor has a very significant voltage drop when "turned on", of the order of one to one-and a half Volts. With the absolute part, I think you mean using a MOSFET such as (IRL540) is "up-to-date". Knowing polarity will be huge in wiring up those LEDs correctly.Thank you for your answers.
Anode and cathode of diode how to#

DIP ICs usually have a notch to indicate which of the many pins is the first. It has two terminals, the anode or positive terminal and the cathode or negative terminal. Through-hole ICs usually come in a dual-inline package (DIP) - two rows of pins, each spaced by 0.1" wide enough to straddle the center of a breadboard. There's a good chance they'll smoke, melt, and be ruined if connected incorrectly. It's very important to keep polarity straight with ICs. Integrated circuits (ICs) might have eight pins or eighty pins, and each pin on an IC has a unique function and position. Next we’ll discuss some of the other common polarized components, beginning with integrated circuits. In this article, we try to look at some methods for diode anode cathode identification. There are tons of parts out there that won’t work if connected incorrectly. If the positive lead touches the anode and negative touches the cathode, the LED should light up.ĭiodes certainly aren’t the only polarized component. The polarity of a tiny, yellow, surface-mount LED is tested with a multimeter. At worst, an incorrectly connected polarized component will smoke, spark, and be one very dead part. If a polarized component was connected to a circuit incorrectly, at best it won't work as intended. A polarized component might have two, twenty, or even two-hundred pins, and each one has a unique function and/or position. You can connect a non-polarized component in any direction, and it'll function just the same.Ī polarized component - a part with polarity - can only be connected to a circuit in one direction.
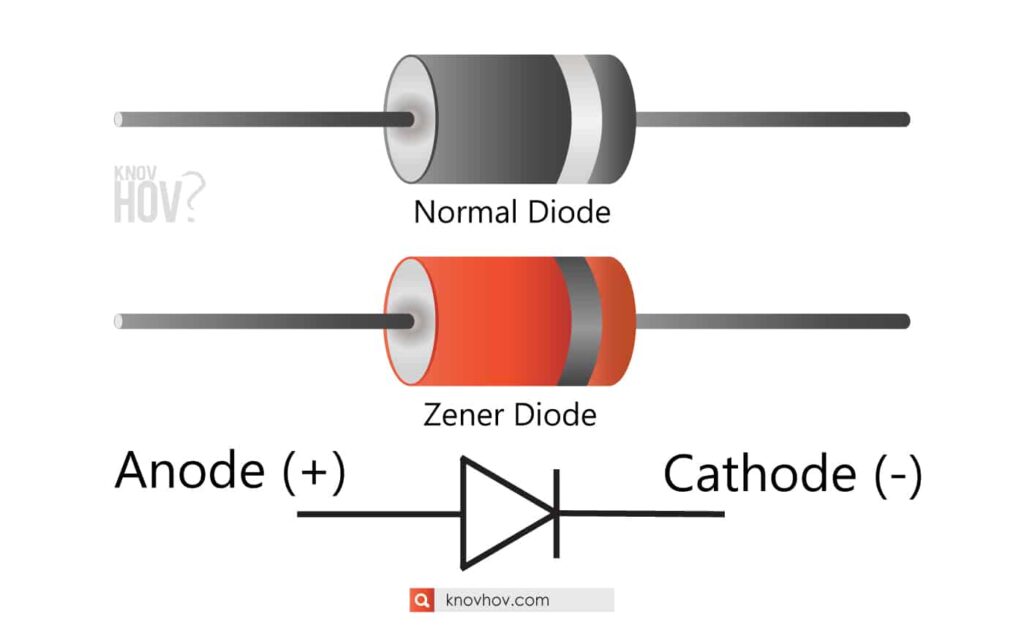
A symmetric component rarely has more than two terminals, and every terminal on the component is equivalent.

A non-polarized component - a part without polarity - can be connected in any direction and still function the way it's supposed to function. In the realm of electronics, polarity indicates whether a circuit component is symmetric or not.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
